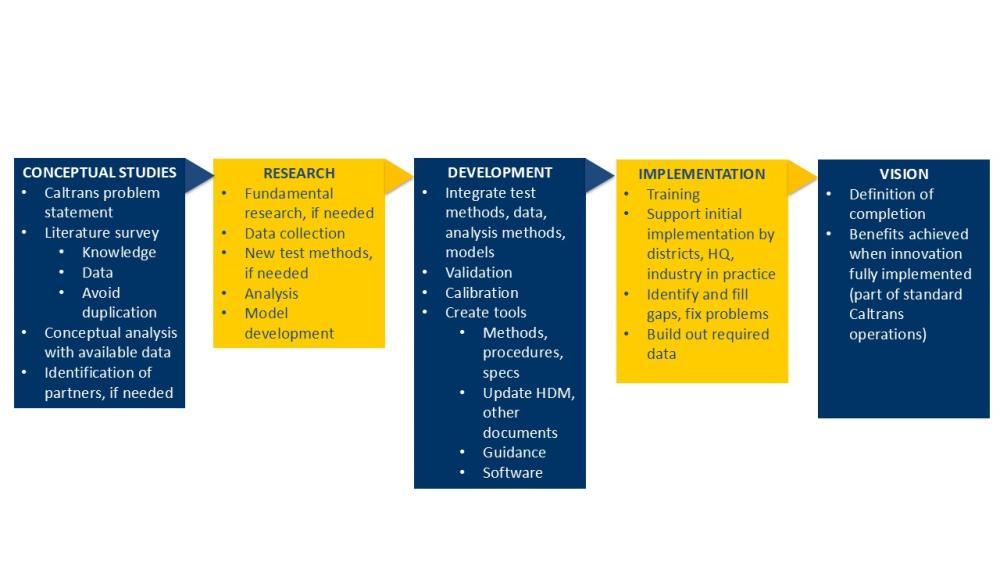
The UCPRC primarily works on projects for the California Department of Transportation. The UCPRC helps move innovation to implementation through four steps: conceptual studies, research, development, and implementation studies. Implementation is defined as the point at which an innovation becomes standard practice. The following is a partial list of UCPRC research implemented by the California Department of Transportation.
Partial list of UCPRC research implemented by Caltrans
Updated 27 September 2025.
Project: Use of RAP in RHMA-G and use of thicker RHMA-G layers
Type of study: laboratory, HVS, field pilots, CalME analysis
Implemented results and dates: 2024 nSSP allowing 10% RAP in RHMA-G, nSSP to be evaluated after UCPRC completes 5 years of monitoring field pilots; 2025 design directive allowing thicker RHMA-G layers.
Project: Balanced mix design (BMD) method development
Type of study: laboratory, field testing
Implemented results and dates: 2024 Caltrans provisional test method 320, to be updated after one year of use in UCPRC laboratory asphalt studies, based on laboratory testing and sampling and analysis of asphalt field sections.
Project: Concrete surfaced pavement design catalogs (jointed plain concrete pavement [JPCP], and short jointed [SJJPCP, a new type])
Type of study: laboratory, HVS, field pilots, modeling using mechanistic-empirical design software and Caltrans PMS data, software development, HDM updates
Implemented results and dates: 2022 updating of Caltrans concrete pavement design catalogs in the HDM, replacing the previous catalogs developed by UCPRC in 2006. Updated catalogs based on calibration of national Pavement ME software using Caltrans 1978-2019 PMS data, HVS testing, and pilot project monitoring of SJJPCP, laboratory testing of typical Caltrans concrete materials properties. Lookup software for the catalog developed but not yet implemented by Caltrans.
Project: Asphalt surfaced pavement design program CalME
Type of study: laboratory, HVS, field pilots, modeling using mechanistic-empirical design software and Caltrans PMS data, HDM updates
Implemented results and dates: 2022 updating of Caltrans software CalME, originally developed by UCPRC in 2006 and implemented in HDM in approximately 2014. Recalibrated using Caltrans 1978-2019 PMS data, HVS testing, and ongoing laboratory testing of typical Caltrans concrete materials properties to update the CalME standard materials library. Included implementation of models for full-depth recycling (FDR).
Project: Pavement management system (PMS) performance models
Type of study: modeling using Caltrans PMS data, software development
Implemented results and dates: 2023 updating of PMS performance models every three years using additional three years of condition survey (APCS) data, traffic data, and construction data. UCPRC also does the updating of the traffic and linear referencing system (LRS) data for the PMS annually.
Project(s): Development of cold recycling technology (full-depth recycling [FDR] and partial-depth recycling [PDR/CIR])
Type of study: laboratory, HVS, field testing and monitoring, mechanistic-empirical performance modeling
Implemented results and dates: UCPRC introduced FDR into California in 2000 and supported the first construction on COL-20 in 2002. UCPRC produced the Caltrans cold recycling guide in 2017 and updated it in 2020 based on HVS and field sections, laboratory testing, and CalME modeling. UCPRC has included cold recycling in the CalME software used by district designers and is continuing to sample and monitor field projects. Also supporting districts on implementation.
Project: Pavement management system engineering configuration
Type of study: set up of the data (traffic, as-builts, condition survey, material types, etc.), performance models, decision tree format, benefit/cost analysis, and reporting of results for use by Caltrans users (PaveM Portal), software development
Implemented results and dates: Implementation began in 2011 and was completed in 2014; periodic updating, and as of 2025, 75% of the PMS operations are being performed using UCPRC code; in 2025/2026, UCPRC is developing code for the remaining 25% as the PMS software vendor software is being phased out by the software owner. Engineering configuration includes global first inclusion of calculation of GHG emissions in a PMS.
Project: eLCAP environmental life cycle assessment (LCA) software
Type of study: life cycle assessment modeling, software development
Implemented results and dates: 2023/2024 training of Caltrans HQ and district staff on use of software; software allows Caltrans to calculate GHG emissions from materials, transport, construction, and effects of roughness on GHG emissions from vehicles. Approach for inclusion in the project development process under development in 2025. Software development began in 2016, and was partially directly funded by the UCPRC when there were breaks in Caltrans funding.
Project: Asphalt performance related specifications (PRS), quality assurance testing, and contractor cost reduction proposal evaluation on Sac-5 reconstruction
Type of study: laboratory, field testing, quality assurance for construction
Implemented results and dates: 2020 to 2022 UCPRC updated the PRS for the asphalt used in the project, supported the district and contractors during mix design development, performed QA testing for performance testing results as designated Caltrans laboratory, and reviewed contractor proposals for pavement under overpasses which resulted in millions of dollars of savings. This is an updating of the PRS approach developed by the UCPRC in 2003 for LA-710 (first Caltrans 30-year design), and in 2012/15 on TEH-5, SOL-80, and SIS-5 (first Caltrans 40-year designs).
Project: Implementation of Superpave asphalt mix design method
Type of study: laboratory, field testing
Implemented results and dates: 2015 replacement of the Hveem method (used since 1950s) as Caltrans standard asphalt mix design method based on UCPRC laboratory comparisons of Hveem and Superpave designed mix performance-related properties.
Project: Pavement and bridge deck designs for reducing traffic noise
Type of study: laboratory, field testing, field section performance monitoring
Implemented results and dates: 2010 changes in Caltrans concrete bridge deck tining from transverse to longitudinal based on UCPRC tire/pavement noise testing; 2012/2014 recommendations to districts for reducing highway noise based on UCPRC tire/pavement noise monitoring of Caltrans asphalt and concrete pavement test sections. Included evaluation of new concrete pavement texture that further reduces noise (monitoring completed in 2023). Included two-year Caltrans/Danish Road Agency partnership facilitated by UCPRC.
Project: Implementation of life cycle cost analysis (LCCA)
Type of study: modeling, software development
Implemented results and dates: UCPRC produced the first Caltrans LCCA manual in 2005 and a Caltrans version of FHWA spreadsheet software. Manual and software updated in 2013, and in 2025 are being updated to web-based software, and consideration of LCCA within a multi-criteria decision analysis framework.
Project: Development of pavement design climate regions and considerations of climate in design, climate region and PG binder maps
Type of study: modeling
Implemented results and dates: The UCPRC evaluated California climate data and its effects on concrete and asphalt pavements in 2000 and then updated the results and developed recommended climate regions with improved pavement temperature modeling in 2004. The UCPRC used the results in 2006 to create the current Caltrans pavement climate regions and supported Caltrans and industry in the development of the asphalt binder PG maps based on the climate regions. The PG map recommendations were updated with more recent climate data and modeling in 2024 that will be included in the near future in an update of the HDM.
Project: 40-year concrete pavement designs, pavement/materials/traffic optimization strategies, and use of rapid-strength concrete for concrete pavement
Type of study: laboratory, field testing, HVS, field monitoring, mechanistic modeling
Implemented results and dates: The UCPRC built test sections for 40-year pavement design concept evaluation in Palmdale in 1998 and tested them with the HVS until 2002. Results were used in the development of the first Caltrans 40-year designs on SBD-15 at Devore, Victorville, and Baker, and RIV-215 between 2002 and 2005. The evaluations included development of an approach for simultaneously considering interactions of concrete materials opening time, pavement design, and traffic management strategies together, now routinely used by Caltrans. Also included evaluation and positive results for rapid strength concrete types in the laboratory and HVS sections, and the use of dowel bars and widened outside lanes.
Project: Warm Mix Asphalt
Type of study: laboratory, HVS, field monitoring
Implemented results and dates: The UCPRC tested two sets of sections with the HVS between 2007 and 2011 to evaluate warm mix asphalt additives and then the same additives in rubberized hot mix asphalt, as well as sampling and monitoring field pilot sections. The positive results led to the inclusion of warm mix in Caltrans standard specifications and a framework for evaluating new asphalt additives.
Project: Dowel bar retrofit on concrete pavement
Type of study: laboratory, HVS, field monitoring
Implemented results and dates: The UCPRC tested field sections between 2000 and 2004 on MEN-101 and LA-14 with the HVS that had dowel bar retrofits as well as control sections. This was combined with laboratory testing of different types of dowels for fatigue and corrosion, and field section monitoring, to make recommendations based on the positive results for continued use of dowel bar retrofit, better attention to grout materials, and use of four dowels in the wheel paths.
Project: Use of mandatory edge drain designs and use of asphalt treated permeable base (ATPB)
Type of study: HVS, field monitoring, mechanistic modeling
Implemented results and dates: The mandatory use of edge drains for asphalt and concrete pavements, and the retrofit of existing pavements, was included in Caltrans standard specifications from the early 1980s based on FHWA recommendations. Between 1995 and 1997, the UCPRC tested with the HVS pavement test sections with and without edge drains (ATPB between base and asphalt combined with perforated pipes surrounded by gravel and a filter fabric under the shoulder) to evaluate their effectiveness. The results showed that the edge drains clogged, the ATPB stripped, and the designs were not effective in improving pavement performance and in fact could often result in worse performance. The results, combined with Caltrans and UCPRC field section investigations, led to the elimination of edge drains and the ATPB layer from standard plans and specifications.
Project: Reflective cracking effectiveness of rubberized asphalt mixes
Type of study: laboratory, HVS, field monitoring, mechanistic modeling
Implemented results and dates: The UCPRC tested two sets of sections with the HVS to evaluate the effectiveness of the Caltrans design of a half thickness of rubberized mix on cracked asphalt in place of a full thickness of conventional asphalt (1997-1998). The results led to more widespread use of rubberized overlays. Another set of sections (2000-2006) evaluated the use of terminal blend rubberized asphalt, and combined with Caltrans field test sections, the results led to the inclusion of terminal blend binders in Caltrans specifications.
Project: Bay Bridge new deck joint testing
Type of study: HVS
Implemented results and dates: In 2011, the UCPRC tested configurations of a new type of bridge deck expansion joint being considered for the new bridge. The HVS test results showed that the new joint design could withstand the design heavy truck loads. The results provided sufficient confidence that the new joints were included in the bridge. As of 2025, they are still performing well.
RELATED ROADMAPS
In-Place and Cold Central Plant Recycling RoadmapME Design of Asphalt RoadmapME Design of Concrete RoadmapPavement Management Systems RoadmapLife Cycle Assessment RoadmapMultifunctional Pavements for Climate Resilience, Urban Environments, and Active Transportation RoadmapLife Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA) RoadmapRoadway Life Cycle Assessment RoadmapRecycled Asphalt Pavement (RAP) and Recycled Asphalt Shingles (RAS) Roadmap Performance-Related Specs for Asphalt SuperPave and QC/QA Roadmap